This application note describes how to program the MCS Bootloader into your AVR and how to use the BASCOM Bootloader application software. MCS Electronics presents | | 
| | Making things easy. |
| | The Bootloading feature in some of the latest AVR devices, gives you the possibilities of programming your AVR's flash thru a serial or USB connection without the need of programming dongles.
At this time BASCOM-AVR has build-in support for these devices:
ATMega8, ATMega88, ATMega168
ATMega16, ATMega162, (ATMega161 mature), ATMega32, ATMega64
ATMega128
Other chips (with Bootloader support) can be added easily to the bootloader.bas example.
Key advantages of the Bootloader:
● Speed up to 115200 Baud
● No additional hardware needed (use an existing RS-232 or USB connection)
● Firmware upgrade without opening the enclosure
● Bootloading over USB (with Linx Module) supported
Disadvantage
● Cannot program fuse and lock bits (can be an advantage in Educational use)
The Bootloader in general
A Bootloader is a piece of software that resides in the AVR's Bootloader memory. The Bootloader memory is a regular part of the FLASH. The Bootloader is not by default present in the controllers memory and needs to be programmed one time using an STK200/300 dongle or any other AVR programmer. Programming the Bootloader program in your controller is only needed once, but you may update the Bootloader program at any time.
After you have programmed the Bootloader you will no longer need an STK200/300 dongle or any other AVR programmer to program the AVR.
Programming the MCS Bootloader
First open the BootLoader.bas file from BASCOM "SamplesBoot" folder.
Select your chip.
$regfile = "m88def.dat"
Const Loaderchip = 88
'$regfile = "m162def.dat"
'Const Loaderchip = 162
This would select the ATMega88. Now compile the program by pressing F7. Then program the Bootloader into the Flash using an STK200/300 dongle or any other programmer (F4). (you only need to do this once).
Make sure to set Fuse bit Q to BOOT and not to Reset vector.
Now in BASCOM-AVR select the 'MCS Bootloader' in the options->programmer window.
You can now use the serial port to program your controller. Or use the Linx USB module in Virtual Com Port mode.
An extensive programming instruction can be found here. Please read chapter 2.3 and 4.
Reset options (DTR or manual)
To initiate a Bootloader programming session, a reset needs to be applied to the controller. You can do this manually, with a reset button or by powering down and up the AVR. But you can also reset your chip using the RS-232 DTR signal. This drawing shows how to connect the AVR to the COM-port.
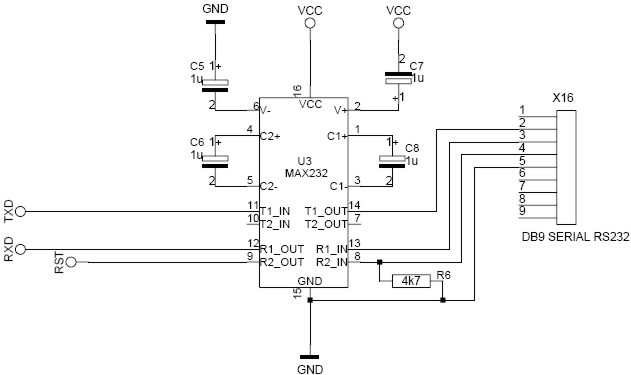 Connections to the AVR
TXD to TXD(0) pin
RXD to RXD(0) pin
RST to RST pin
| Connections on the DB9 connector FEMALE
2. RS232-RXD
3. RS232-TXD
4. RS232-DTR
5. RS232-GND |
Notice the 4k7 resistor that prevents your controller from reset state if no computer is connected at the other end of the cable.
Speed and oscillator considerations
You can select baud rates up to 115200. It is important however that you have chosen a Baud /crystal combination that has a 0% error margin. You can find the error margins in Atmel datasheets. For the ATMega88 these section of the datasheet is extracted here.
If you use an internal oscillator we suggest you start with 38400 Baud. If your AVR runs on a high frequency oscillator (16 MHz) you should change the timeout in the Bootloader.bas program to 200000.
$timeout = 200000
Downloads
Instead of using the BASCOM-AVR build in programmer you can also use our stand alone Bootloader application. Which is free of charge.
● MCS Bootloader
Atmel Bootloader application notes
On the Atmel web site you can find Bootloaders that encrypt your firmware. We do not provide support for the Atmel application notes. For Atmel application notes click here.
| |
|
|
